
Nutrition 101
There’s a lot of myth and pseudoscience surrounding nutrition and health that make healthy eating seem complicated and overwhelming. We are going to simplify nutrition and stay in the science we know so you can have some practical knowledge today
Understanding Macronutrients: The Essentials of a Balanced Diet
When you hear the term "macronutrients," you might think it sounds complicated, but it's actually a pretty straightforward concept. Simply put, macronutrients are the nutrients that our bodies need in large amounts to function properly. They are the fundamental building blocks of our diet, and they play crucial roles in keeping us healthy and energized. There are three main types of macronutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Let's break down each one and see how they contribute to our well-being.
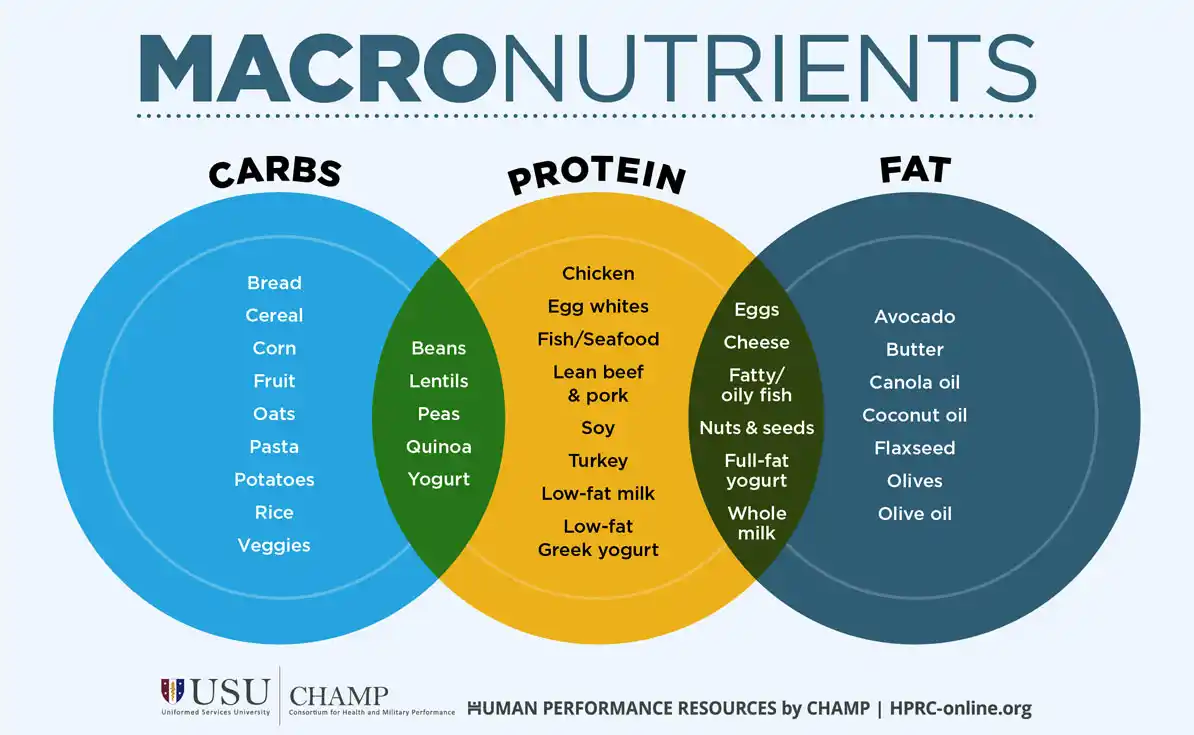
1. Carbohydrates: The Body's Main Fuel Source
Carbohydrates are energy. Your brain and muscles both use this as fuel. Proteins must be turned into carbs to be used as energy. When you eat more carbs than you are using, you feel lethargic and your body stores the energy as body fat. Avoid eating carbohydrates by themselves to keep your blood sugar and energy levels stable
Examples of Carbohydrates:
Fruits: Apples, bananas, berries
Vegetables: Potatoes, corn, peas
Grains: Bread, rice, pasta, oats
Legumes: Beans, lentils, chickpeas
Sweets: Pastries, ice cream, candy, cereal
2. Proteins: The Body's Building Blocks
Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues, making hormones, and supporting immune function. Think of proteins as the body’s sheetrock, wood, tile, bricks, etc.; eating proteins and fats before carbs in a meal is much more healthy by keeping your blood sugar even.
Examples of Proteins:
Meat: Chicken, beef, pork
Fish: Salmon, tuna, trout
3. Fats: Essential for Energy and Cell Health
Fats often get a bad rap, but they are actually crucial for many bodily functions. They provide a longer lasting source of energy, help absorb certain vitamins, build your hormones, and are essential to maintain healthy cell membranes. Fats provide long term energy
Examples of Fats:
Healthy Fats: Avocados, olive oil, avocado oil (best for cooking with), nuts, seeds
Animal Fats: Butter, fatty cuts of meat, cheese
Processed Fats: Many baked goods, fast food, and snacks contain trans fats or high amounts of saturated fats.
Minimize animal fats and only eat processed fats monthly or less.
Balancing Your Macronutrients
Make sure every meal has proteins, fats, and carbs and you’ll enjoy more stable energy levels and better overall health. Balancing your macros and eating healthy sources of each will prevent diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and even decreases your risk of cancer and increases your chances of surviving cancer.
Images obtained from
Andrea Piacquadio
https://health.mil/News/Gallery/Infographics/2022/06/22/macronutrients




